What Is Network Address Translation (NAT)?
Network Address Translation in short NAT is the way of mapping multiple internal private IP addresses to a public one IP before transferring the information to the internet. The main objective of Network Address Translation (NAT) is to conserve the number of registered public IP addresses of IPv4. Network address translation allows a single device (such as Router or NAT firewall) to act as the agent between the local internal (private) network and the external (public) network that is the internet. Mostly corporates that want multiple devices to employ a single IP address use Network Address Translation, similarly our home router also uses Network Address Translation, so that all devices which are connected to it easily exchange the data to the internet.
What Is the Purpose of Network Address Translation (NAT)?
The main purpose of Network Address Translation is conservation of IP Addresses. The current IP version “IPv4” uses 32-bit numbered IP addresses, which store more than 4 billion IP addresses, which sounded like more than enough but as the internet expanded and went global, we quickly ran out of addresses, Today is the era of smartphones, smart television, smart printer, tablet, IoT devices, even refrigerators all are required an IP address to connect internet. We cannot access internet via private IP address we need a public IP address to access the internet.
On June 2012, engineers introduced a new version of IP called IPv6. IPv6 is next generation Internet Protocol standard based on 128-bit addressing and capable of support 340 undecillion (340 trillion3 addresses) but it will take several years to alter the current networking system infrastructure and implement. Until then, we can implement NAT for access internet with private IP address, to read more about Internet Protocol version 6(IPv6) click here.
Working of Network Address Translation (NAT)
We already know that private IP does not allow us to access internet, to access internet we need public IP or a registered IP address to access internet. Suppose an organization has two devices.
Device A has Private IP Address “10.1.1.1”.
Device B has Private IP Address “10.1.1.2”.
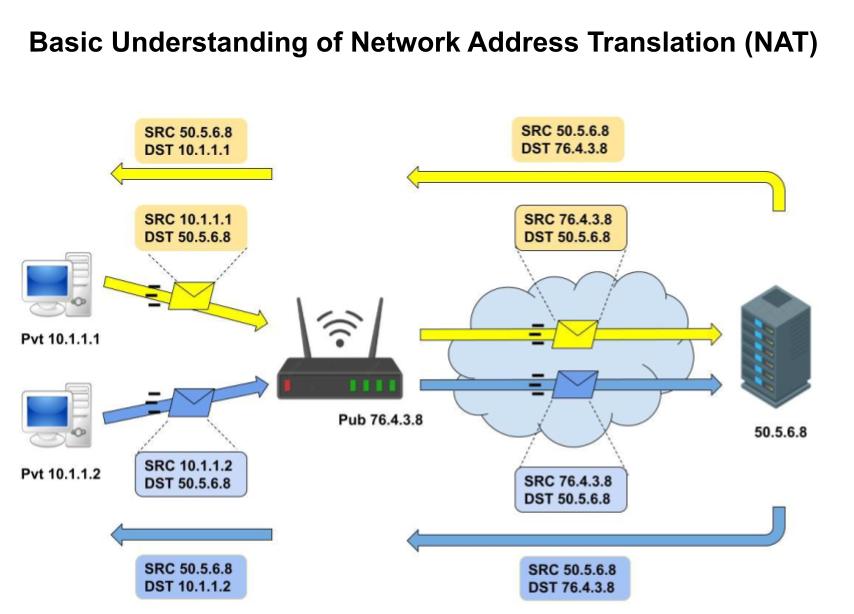
Both devices want to access the Facebook server which has the IP address “50.5.6.8”. But they can’t reach the Facebook server via a private IP address. But we know that router has a public IP assigned by Internet Service Provider (ISP), NAT maps both private IPs to the router’s public IP. Now router acts on behalf of both devices. So that both devices easily access the Facebook server as shown in the above figure.
When the Facebook server received packets then it will not directly respond to both devices it will respond to the only router and the router forward server responds to both devices which have only private IP. As a result, both devices are now able to access to the internet with the help of NAT.
Types of Network Address Translation (NAT)
1. Static Network Address Translation SNAT
Static NAT is also known as one to one NAT. Static NAT is used for one-to-one mapping of a private IP address to a public IP address. Below there is an example of Static NAT. It puts a permanent mapping between private IP address and a public IP address means private IP “10.1.1.1” always mapped with public IP “76.4.3.7”. Similarly for others 10.1.1.2 IP always mapped with 76.4.3.8 IP and 10.1.1.3 IP always mapped with 76.4.3.9 IP.

2. Dynamic Network Address Translation DNAT
In Dynamic NAT, multiple private IP address is mapped to a public IP address from a group of public IP addresses called as NAT pool. The private to public IP mapping depend upon the available public IP address in NAT pool. For example private IP “10.1.1.1” mapped with public IP “76.4.3.1” and private IP “10.1.1.2” mapped with public IP “76.4.3.5”. All translation is random in dynamic NAT as shown in below figure.

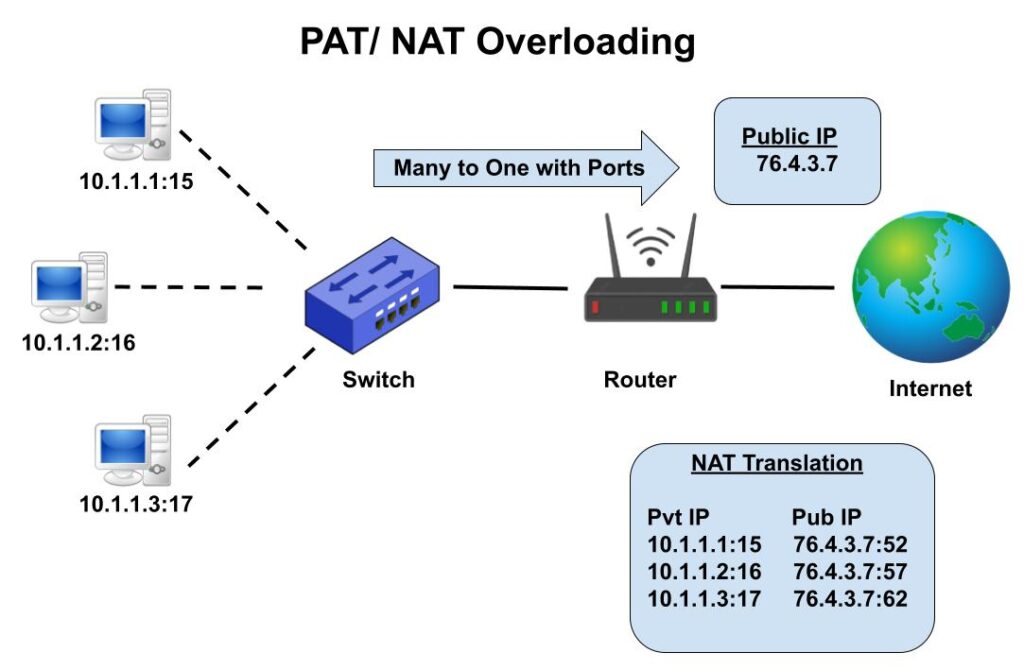
3. Port Address Translation PAT
It is also known as NAT Overloading. In PAT many Private IP Addresses are translated to one Public IP Address and port numbers are used to distinguish the traffic i.e., which traffic (packet) belongs to which IP address. For example private IP 10.1.1.1:15 translated to public IP 76.4.3.7:52. Similarly IP 10.1.1.2:16 mapped with same public IP but different port number i.e. 76.4.3.7:57.
Advantages of Using Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) provides more security and privacy to the user by hiding the device IP addresses from the outside network, even when you sending and receiving traffic.
By using Port Address Translation (PAT), it conserves IPv4 addresses that are legally registered and prevents their depletion. By not using the global IP address in the local addressing.
With the help of NAT many organization reduces their cost because no need to buy new IP addresses for all the computers they have in their environment. They assign same IP address to the all computes with different port numbers and save huge amount of money.
If we compare the NAT with Proxy both hide our private device address but proxy work at OSI layer 4 which also known as transport layer due to which it slow down the information exchange while NAT which is a network layer or layer 3 protocol, making exchange faster.
Network Address Translation provides increased flexibility when connecting to the public Internet and it is highly scalable. It is easily configured with dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) server and router.
Disadvantages of Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network address translation is a technology that consumes processor and memory resources because it translates private IP address to the public address during outgoing and translate public IP address to private IP address during incoming traffic. Also store all information in memory.
By using NAT, we loss the end to end IP traceability. In NAT IP address changes so many times and it will make troubleshooting more complex.
Some technologies and network applications are not compatibility with NAT.
Related Contents
1. What is an IP address?
2. Difference between IPv4 & IPv6.
3. Difference between Public and Private IP Address.
4. What is DHCP Server?
5. What Is DORA Process in DHCP?
6. What is DNS Server and How Its work?
7. What is Ports and Protocols in computer networks?
8. How Proxy Server hides IP Addresses?
9. What is Firewall?
10. How DNS Server related to IP Address?
11. IDS Vs IPS in Security.
12. Difference between Hub, Switch & Router.

